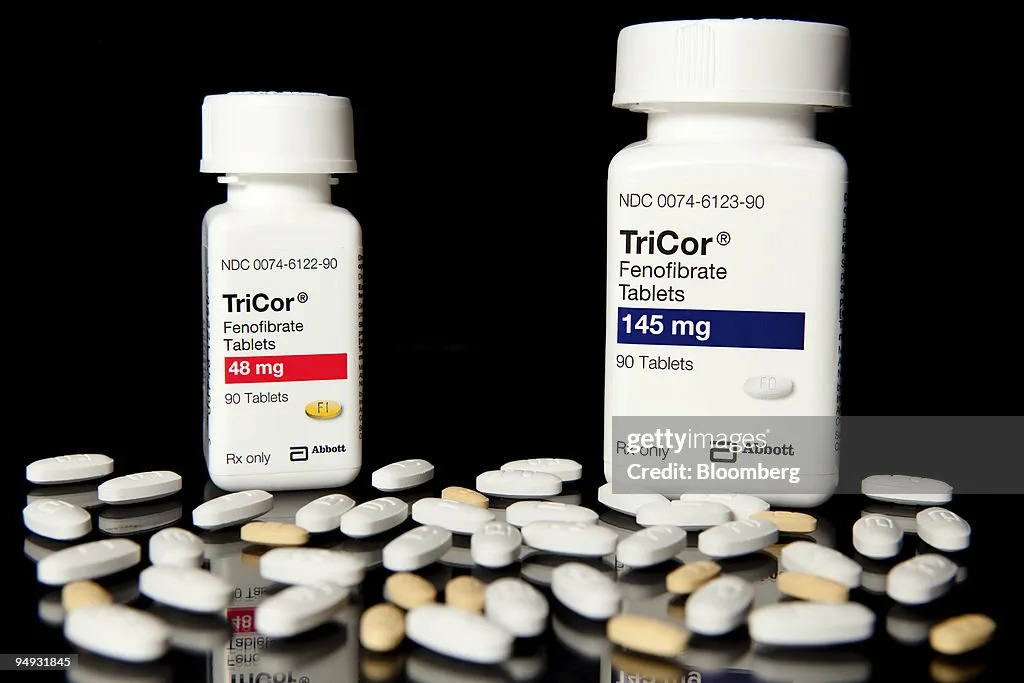
Tricor - Product Description
Overview:
Tricor (fenofibrate) is a fibrate class medication used to manage high triglyceride and cholesterol levels, particularly in patients with hypertriglyceridemia or mixed dyslipidemia. It works by enhancing the breakdown of fats in the blood and reducing triglyceride production in the liver. Tricor is especially effective in preventing pancreatitis by significantly lowering triglyceride levels. Additionally, it helps reduce LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol, providing comprehensive lipid management. Tricor is usually taken once daily, with or without food, and requires regular monitoring of lipid levels and liver function to ensure safety and effectiveness. Its targeted triglyceride reduction and compatibility with other lipid-lowering therapies make Tricor a valuable option for patients with complex lipid disorders.
Indications:
Tricor is indicated for the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia (high triglycerides) and mixed dyslipidemia, conditions associated with abnormal lipid levels in the blood. It is particularly beneficial for patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia, who are at risk for pancreatitis, a potentially life-threatening condition. Tricor is also used to lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol, making it a comprehensive option for managing lipid levels. Patients who do not achieve adequate lipid control through diet and lifestyle changes alone may benefit from Tricor’s lipid-lowering effects. Its use is particularly recommended in patients at high risk for cardiovascular events due to dyslipidemia.
How to Use:
Tricor is typically taken once daily, with or without food, as prescribed by a healthcare provider. It’s important to take the medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s dietary recommendations while on Tricor to enhance the medication’s effectiveness. Regular blood tests are required to monitor lipid levels and liver function, ensuring that Tricor is working as intended and not causing any adverse effects. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible unless it is close to the time for the next dose. Consistency in taking Tricor is key to achieving optimal lipid control.
Advantages:
Tricor offers several advantages, including its potent effect on lowering triglycerides, which is crucial for preventing pancreatitis and reducing cardiovascular risk. It also provides comprehensive lipid management by lowering LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol. Tricor’s compatibility with other lipid-lowering therapies makes it a versatile option for patients with complex lipid profiles. Its effectiveness, combined with its ability to be integrated into broader treatment plans, makes Tricor a valuable medication for long-term lipid management.
Conclusion:
Tricor is a powerful medication for managing high triglyceride levels and mixed dyslipidemia. By significantly lowering triglycerides and addressing other lipid levels, Tricor helps prevent serious conditions like pancreatitis and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its proven efficacy, combined with its ability to be used alongside other lipid-lowering therapies, makes Tricor an essential part of comprehensive lipid management. Regular monitoring and adherence to prescribed dosing are vital to maximize the benefits of Tricor. It remains a trusted option for patients requiring targeted and effective lipid control.
Composition:
Tricor contains fenofibrate as its active ingredient, which works by activating an enzyme that breaks down fats in the blood, thereby lowering triglycerides and improving cholesterol levels. The inactive ingredients in Tricor may include lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, and magnesium stearate, among others, which help stabilize the medication and ensure proper absorption. Tricor’s formulation is designed to effectively manage lipid levels, providing essential protection against pancreatitis and cardiovascular disease.
Note:
Patients taking Tricor should be aware of potential side effects, including gastrointestinal issues, liver enzyme elevations, and muscle pain. Regular monitoring of liver function and lipid levels is necessary to ensure the medication’s safety and effectiveness. Tricor should not be used in patients with severe kidney or liver disease. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid using Tricor due to potential risks to the fetus or infant. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications and supplements they are taking, as Tricor can interact with other drugs. Adhering to a healthy diet and lifestyle is important to complement the lipid-lowering effects of Tricor.